Just determining whether the $112 million in uncollectible accounts is a relatively high or low figure is quite significant in evaluating the efficiency of Dell’s current operations. There are a few steps involved in calculating the net realizable value for an asset. First, you’ll have to determine the expected selling price or the market value. Keep in mind that this should follow the conservatism principle in accounting. These examples show how NRV helps businesses determine the actual value they can expect from their assets, whether it’s inventory or accounts receivable.
Decommissioning and restoration costs form part of inventory costs under IAS 2; not under US GAAP
This is obtained when the disposable costs related to sales is subtracted from the selling price of an asset. Based on this figure obtained, the firms determine the value of their asset. When doing the NRV calculations for accounts receivable, the allowance for doubtful accounts or bad debts takes the place of total selling costs. Net realizable value is a critical concept in accounting, used to ensure that the value of assets on financial statements is not overstated. Here, we explore the application of NRV in different accounting contexts, including inventory valuation, accounts receivable, and cost accounting. When inventory is measured as the lower of cost or net realizable value, it is embracing the accounting principle of conservatism.
- This helps stakeholders make informed decisions and maintain trust in the company’s financial reporting.
- For example, certain industries may necessitate dealing with customers that have riskier credit profiles, thus forcing the company to experience larger write-off allowances.
- NRV is a common method used to evaluate an asset’s value for inventory accounting.
- This allows managers to calculate the total cost and assign a sale price to each product individually.
- Entities shall not measure physical inventories at fair value, except as provided by guidance in other Topics.
Order to Cash
NRV is a common method used to evaluate an asset’s value for inventory accounting. Two of the largest assets that a company may list on a balance sheet are accounts receivable and inventory. NRV is a valuation method used in both generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and international financial reporting standards (IFRS). Net realizable value (NRV) is the the custodial parent amount by which the estimated selling price of an asset exceeds the sum of any additional costs expected to be incurred on the sale of the asset. NRV may be calculated for any class of assets but it has significant importance in the valuation of inventory. Both GAAP and IFRS require us to consider the net realizable value of inventory for valuation purposes.
Subscribe to the IFRS® Perspectives Newsletter
In either situation (high inflation or high unemployment), it may be more difficult for clients or businesses to find budget for additional goods to buy. Depending on the industry the company is it, the company may decide to accept a certain amount of uncollectable sales. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB® Board) eliminated the use of LIFO because of its lack of representational faithfulness of inventory flows. Energy trading contracts that are not accounted for as derivatives in accordance with Topic 815 on derivatives and hedging shall not be measured subsequently at fair value through earnings.
What are costing techniques?
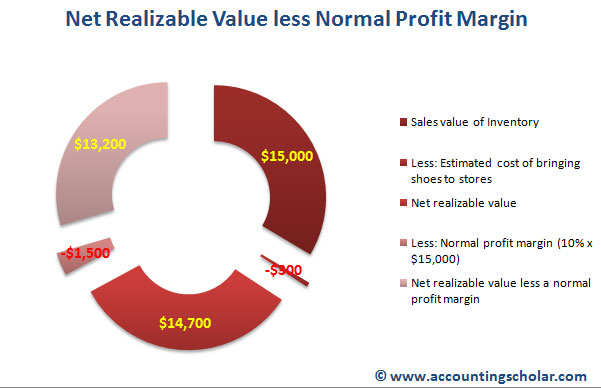
If the market price of inventory fell below the historical cost, the principle of conservatism required accountants to use the market price to value inventory. The expected selling price is calculated as the number of units produced multiplied by the unit selling price. This is often reduced by product returns or other items that may reduce gross revenue. It can also simply be done for just a single item rather than a group of units. In regards to accounts receivable, this is equal to the gross amount to be collected without considering an allowance for doubtful accounts. Thus, the amount of cash that is estimated to be received is the reported $4.731 billion balance ($4.843 billion total less $112 million expected to be uncollectible).
Scope of onerous contracts requirements is broader under IFRS Standards than US GAAP
Although we endeavor to provide accurate and timely information, there can be no guarantee that such information is accurate as of the date it is received or that it will continue to be accurate in the future. No one should act upon such information without appropriate professional advice after a thorough examination of the particular situation. Under IAS 2, inventory may include intangible assets that are produced for resale – e.g. software. Like IAS 2, transport costs necessary to bring purchased inventory to its present location or condition form part of the cost of inventory.
The cost to prepare the widget for sale is $20, so the net realizable value is $60 ($130 market value – $50 cost – $20 completion cost). Since the cost of $50 is lower than the net realizable value of $60, the company continues to record the inventory item at its $50 cost. The conservative recordation of inventory values is important, because an overstated inventory could result in a business reporting significantly more assets than is really the case. This can be a concern when calculating the current ratio, which compares current assets to current liabilities. Lenders and creditors rely on the current ratio to evaluate the liquidity of a borrower, and so might incorrectly lend money based on an excessively high current ratio. Further, writing down inventory prevents a business from carrying forward any losses for recognition in a future period.
For any company, accounts receivables and inventory are the two asset forms that it maintains. The NRV analysis that companies perform is accepted by generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) as well as International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). NRV is the valuation method which is adopted by the firms to ensure they price the assets properly.
